IPv4 vs IPv6: What are they and what's the difference?
The Internet Protocol (IP) is one of the most important communication protocols in the Internet Protocol Suite (IPS), which is used for routing and addressing packets for networking devices such as computers, laptops, and fiber switches across a single network or a series of interconnected networks. What will happen if we eventually run out of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses? There are currently two versions of Internet Protocol: IPv4 (IP version 4) and IPv6 (IP version 6). What do IPv4 and IPv6 mean? Is IPv6 in fact superior to IPv4? Read on to find out!
What is IPv4?
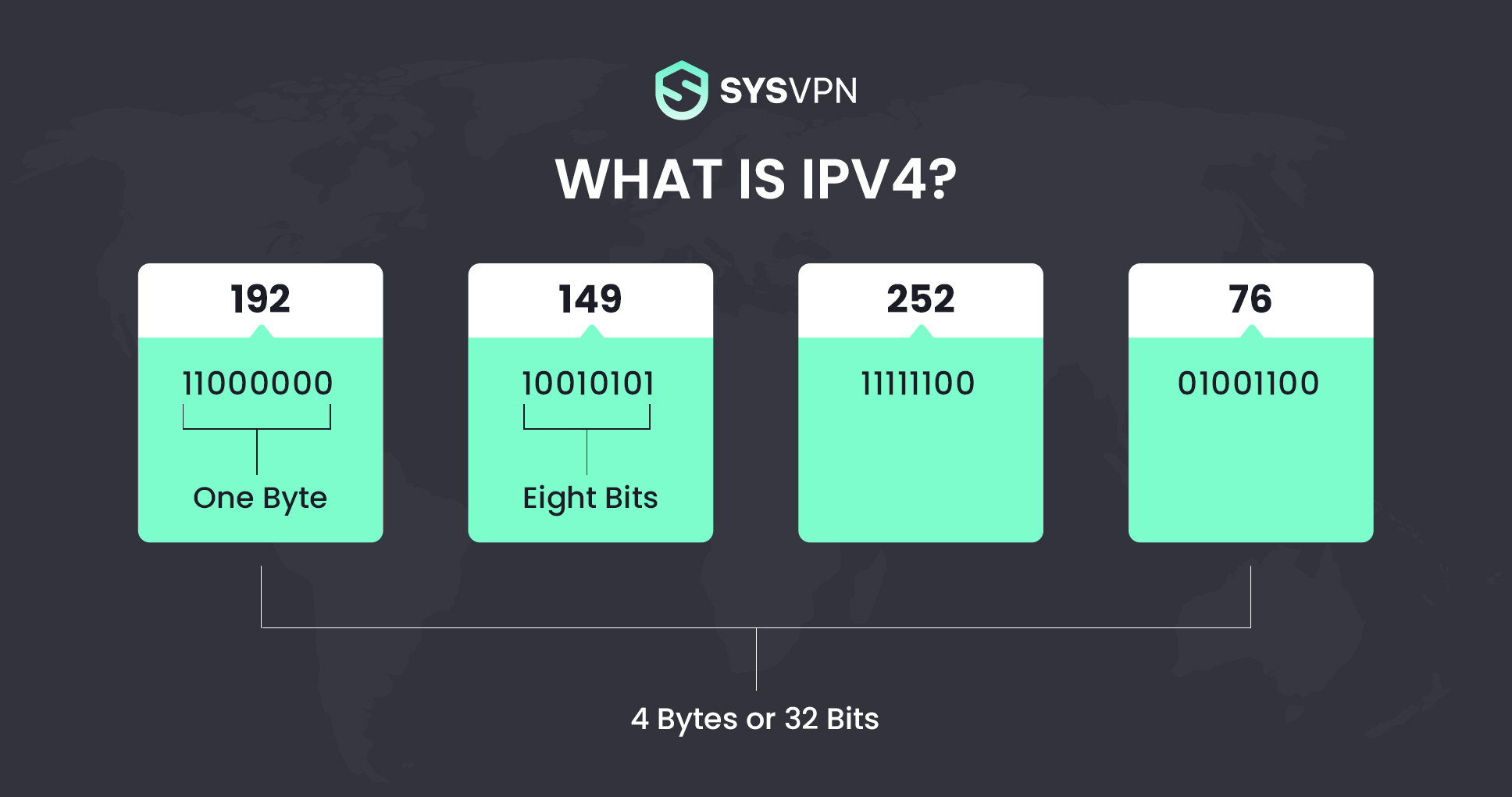
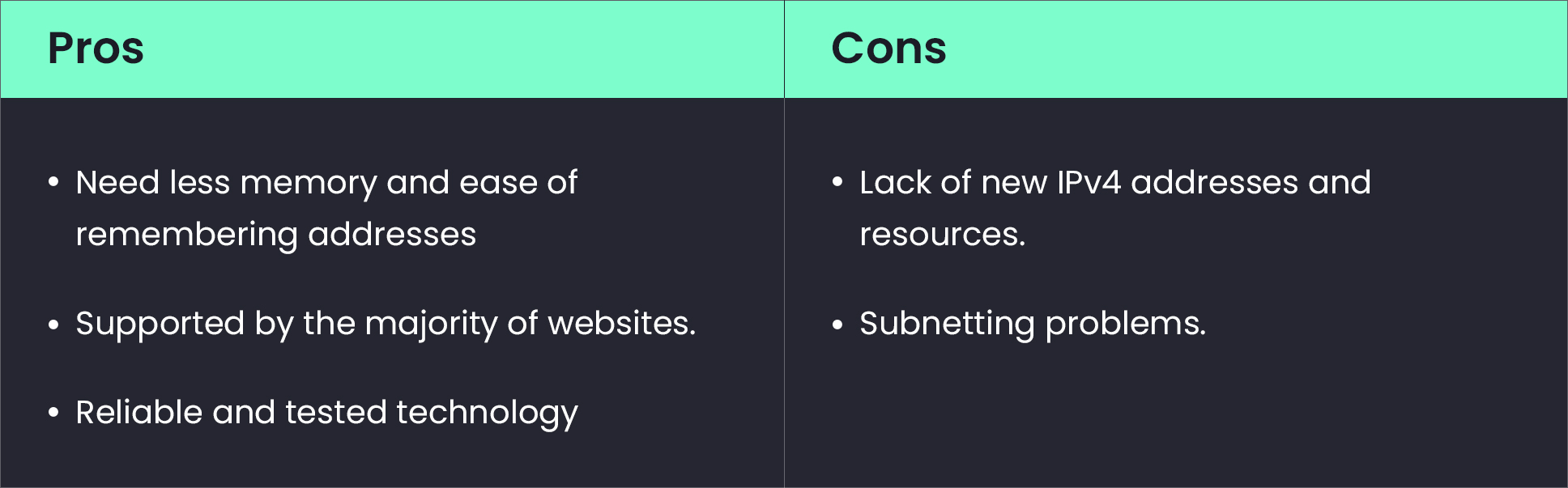
IPv4 was the first widely used version of IP addresses. IPv4 is the current protocol used to generate, assign, and use IP addresses. Due to the 32-bit addressing used by this protocol, it is possible to assign up to 4.3 billion unique addresses. However, engineers who developed IPv4 40 years ago could not foresee a world in which millions of people would each have at least a few internet-connected devices. Clearly, there won't be enough IPv4 addresses (IPs) for the world's population to use. As more and more people utilize the internet, IPv4 addresses are being used up. We are running out of IPv4 addresses. In order to meet the need for additional Internet addresses, the new Internet addressing system, IPv6, is being deployed.
Features of IPv4
- In IPv4, IP addresses look like four one-byte decimal numbers, separated by a dot. Such as 182.178.1.1.
- IPv4 allows connectionless protocol by creating a layer of simple virtual communication over a variety of devices.
- Offers video libraries and conferences.
What is IPv6?
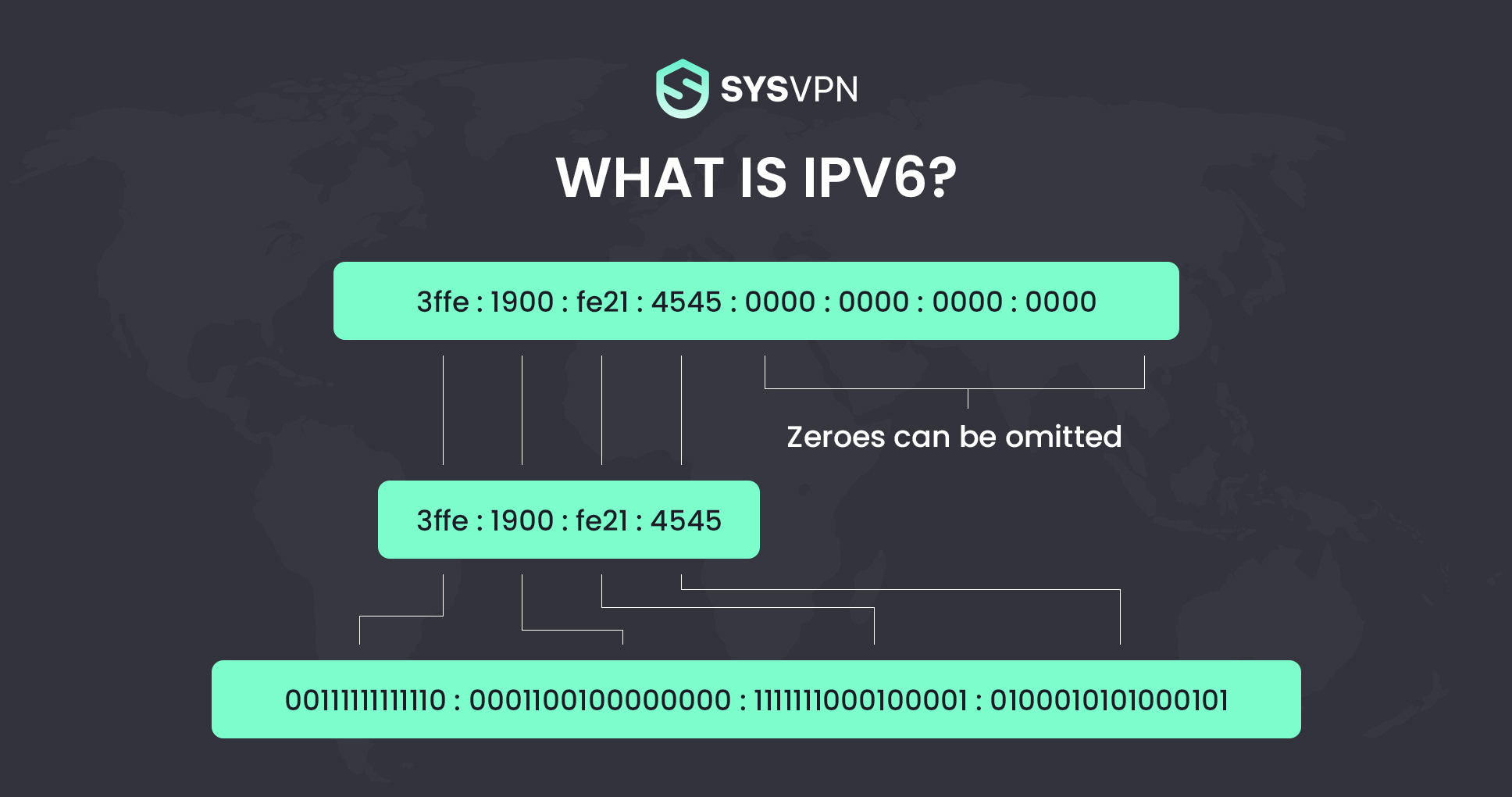
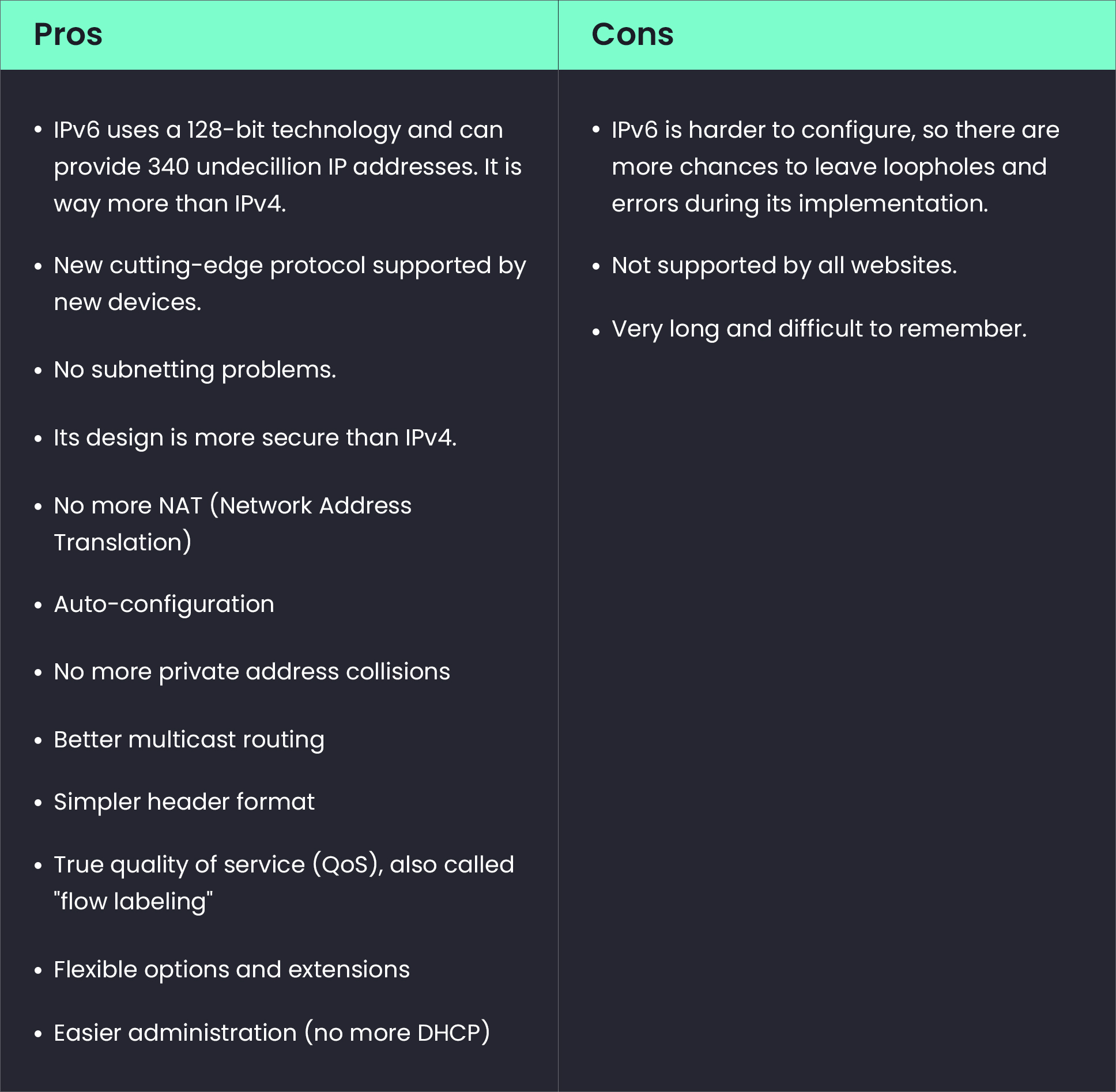
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the sixth revision to the Internet Protocol and the successor to IPv4. It functions similarly to IPv4 in that it provides the unique IP addresses necessary for Internet-enabled devices to communicate. However, it does have one significant difference: it utilizes a 128-bit IP address means it can generate 3.4 × 1038 addresses. The number of IPv6 addresses is 1028 times larger than the number of IPv4 addresses. So there are more than enough IPv6 addresses to allow for Internet devices to expand for a very long time.
Features of IPv6
- The text form of the IPv6 address is xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx, where each x is a hexadecimal digit, representing 4 bits. Leading zeros can be omitted. The double colon (::) can be used once in the text form of an address, to designate any number of 0 bits.
The differences between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
IPv4 and IPv6 are both types of addresses that may be used to identify network-connected devices. Both are based on the same common ground, yet operate in quite different ways. What are the key distinctions between them? The primary differences between IPv4 and IPv6 are shown in the following table.
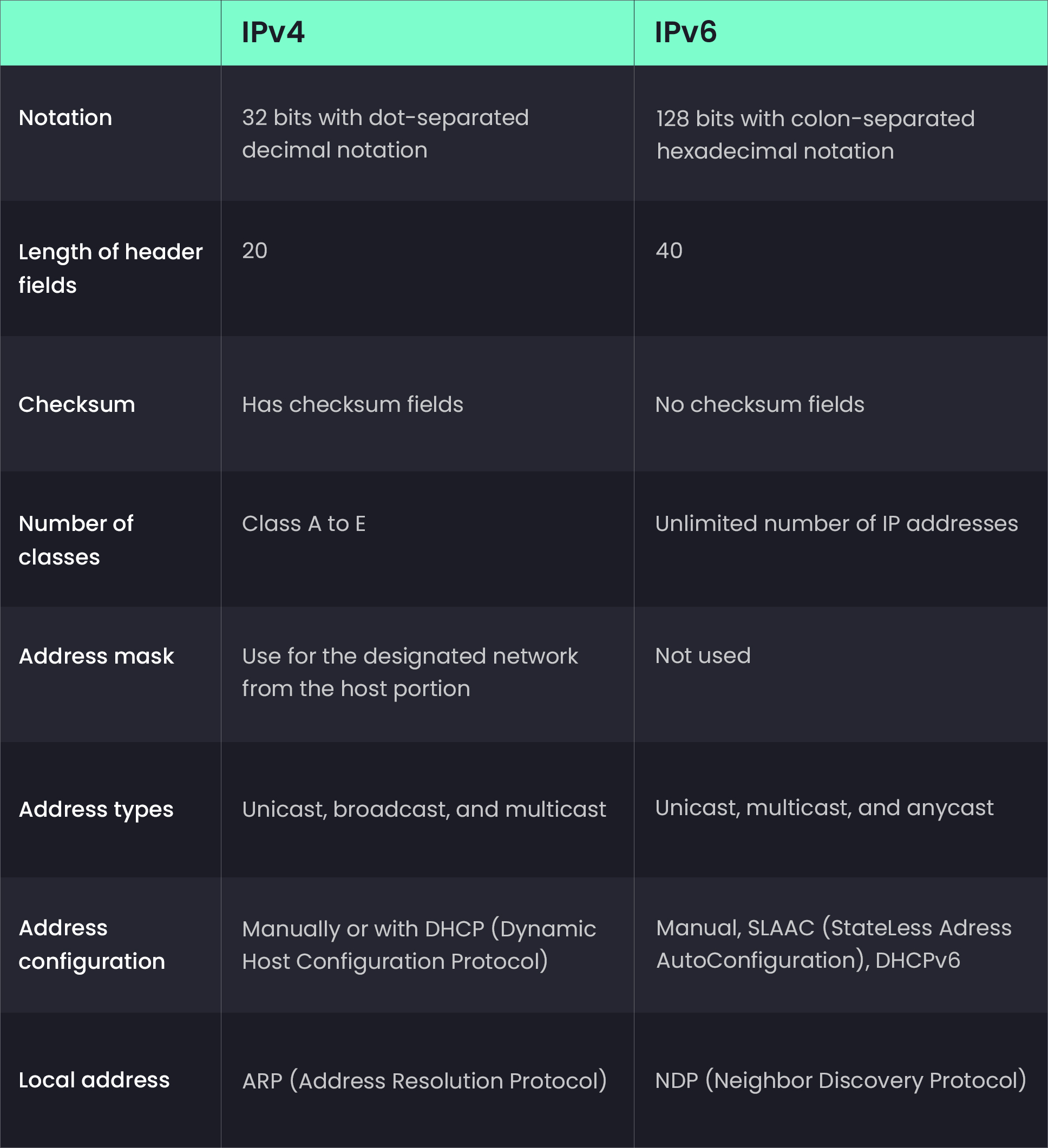
The similarities between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
Here are some parallels between IPv4 and IPv6 technologies:
- Both IP addresses are composed of binary digits and are used to identify network-connected devices.
- Each allows for manual IP assignment.
- Each IP system utilizes a packet header and is capable of transmitting fragmented packets.
- Each is capable of broadcasting and multicasting.
- Each supports VLSM.
Is IPv6 better than IPv4?
1. Improved Security
IPv6 was designed with safety in mind. It ensures the privacy of the data while also providing authentication and maintaining its integrity. Due to concerns that IPv4's Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) can be used to spread malware, it is often blocked by corporate firewalls. However, IPv6 ICMP packets may use IPSec, significantly enhancing their security.
IPv6 relies on IPSec for network security, while with IPv4 it is either not necessary or comes at an additional expense. When using this IPv6 function, your network's data will be more consistent, more secure, and more private.
2. No geographical limitations
IPv6 addresses will be globally distributed, unlike IPv4 addresses, which were allocated on a regional basis. When IPv4 was created, half of all addresses were set aside for use in the United States.
3. Possibility of more efficient routing (IP Header Format: Lower Size of Header Bandwidth)
IPv6 headers are lengthier but more consistent than IPv4 headers, which are variable. This might simplify the code for routing to these addresses and reduce the amount of hardware processing required. Here, IPv6 would provide superior service quality and a more satisfying end-user experience.
Extended headers make IPv6 addresses four times bigger than their predecessor, the IPv4 address. This additional characteristic of the IPv6 address reduces the overhead of packet processing and header bandwidth, hence accelerating the connection.
4. End-to-end connectivity (Network Security: Faster Speed and Lack of NAT)
The Network Address Translation (NAT) technique was developed by engineers as a possible solution to the problem of insufficient IP addresses. IPv6 would provide enough IP addresses for all devices, which would render NAT no longer necessary. Now, any gadget may connect to the internet and "communicate" directly with websites.
IPv6 is quicker on network devices than IPv4 because it eliminates network-address translation (NAT). If you need a quick network processing time, IPv6 is the way to go.
5. Auto-configuration
The stateless auto-configuration is widely considered to be one of the most beneficial aspects of IPv6. This enables devices to self-assign IP addresses without requiring a server. Instead, IP addresses are established by utilizing the device's media access control (MAC) address, which is unique to each and every mobile device, laptop, and desktop computer you possess. This facilitates device discovery amongst devices linked to the same network.
IPv6 is incompatible with IPv4
You won't be able to visit a website that is operating on IPv4 if both your device and your internet service provider only support more recent versions of the protocol, IPv6. In order to access the website, your device must also be IPv4-compatible.
IPv6 is supported by the vast majority of current routers and electronic devices; nevertheless, in order to accomplish a seamless transition throughout the globe, all devices, operating systems, and Internet service providers will need to upgrade their systems. They will need to continue running both protocols for some time in order to prevent any interruptions in service, which may result in additional costs.
It is not clearly obvious how these advantages will help the normal user
If customers don't see the effects of or perceive the value of new technology, it's challenging for businesses to justify spending money on it. The generation of more IP addresses is a worthwhile and long-term objective, but it won't have an impact on regular users until we really deplete the pool of available addresses.
What version of IP protocol (IPv4 or IPv6) should I enable?
You are able to utilize both IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously. Browsers check to see whether a website supports IPv6. In such case, they will submit a request using IPv4 protocol.
IPv6 and VPNs: Does it matter if your VPN doesn't support IPv6?
You may be wondering how IPv6 relates to VPNs. Unfortunately, several major VPN companies, including SysVPN, do not truly support IPv6. If, on the other hand, you connect to the VPN using an IPv4 address, everything should go off without a hitch; your data will be safeguarded as it goes over via the encrypted tunnel with IPv4 protocol.
The vast majority of VPN apps are IPv4-only. If you were to try utilizing IPv6 over an IPv4-only VPN, it would presumably reroute your IPv6 traffic via the default gateway and ISP. Using IPv6, your data would leave the protected VPN connection.
Currently, our solution includes disabling the majority of IPv6 traffic to protect the security of user traffic. Nevertheless, IPv6 functionality is in SysVPN's roadmap.



